Many doctors joke that prostatitis is male menopause. This disease is diagnosed in 20% of cases in men after forty years, in 70% - after sixty years, and in 90% of cases after seventy years. The disease can come in two forms: acute and chronic prostatitis. This disease needs treatment, especially since it lends itself well to therapy. However, many men ignore unpleasant symptoms, which leads to the development of many complications, which it becomes more difficult to cure.
Reasons for development
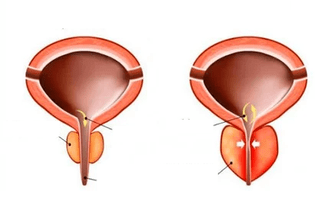
Acute prostatitis is an acute pathology of the prostate that develops as a result of an inflammatory and infectious process in an organ due to the penetration of pathogens into its tissues. The disease is characterized by the appearance of swelling of the gland, purulent contents in its tissues.This leads to the appearance of many unpleasant symptoms and a disruption of the functionality of the organs of the genitourinary system.
There are many causes of acute prostatitis. In most cases it is provoked by pathogenic microbes.Some of the microbes can be passively present on the skin or in the intestines in a healthy person. Under the influence of some factors, they are activated, penetrate the tissues of the gland and actively multiply there. Often times, the disease occurs due to sexually transmitted diseases, such as: B.Chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, gonorrheaetc.
An acute form of prostatitis also occurs as a complication ofurethritis. Germs enter through ducts that open into the urethra. The spread of bacteria from other organs of the genitourinary system also often becomes the cause of the occurrence of prostatitis. Often the gland can be affectedduring surgical interventions, catheterization, diagnostic measures.
Since the prostate contains a large number of blood vessels, an infection with the blood flow can occur in chronic pathologies in the body, e. g. B.tonsillitis, bronchitisetc.Ifanal fissuresare present, microbes can enter the prostate with lymph flow.
However,infections do not always lead to the development of diseases. Congestion in the vessels of the pelvic region, whichdevelops with prolonged abstinence from sexual intercourse or a large number of them.
Overwork is also associated withlack of physical activity, constant constipation, alcoholism, varicose veins in the pelvic area and hypothermia.
Classification
In urology, different forms of pathology are distinguished, which also represent their developmental stages:
- Catarrhal formis characterized by the occurrence of inflammation in the organ, a change in the mucous membrane epithelium. Over time, the swelling of the gland appears, a mucopurulent secret is collected in it, which contributes to the progression of the disease.
- Then the focal suppuration appears. The disease enters the second stage (form) -follicular form. The urinary tract is narrowed or blocked, the secret is usually no longer excreted from the organ. Pus can pass into the urinary tract and form purulent foci there. The cells of the gland change, the prostate continues to swell and grow in size.
- Parenchyma formdevelops when the organ is completely inflamed and a purulent infection develops in it. Without therapy, small purulent foci merge into one large one, creating an abscess, which often opens into the urethra, intestines and bladder. In some cases, if the infection enters the interstitial tissue of an organ with a flow of blood or lymph, it is possible to develop this form of pathology immediately.

Symptoms
Shows symptoms of acute prostatitis. How strong the signs are visible and noticeable depends on the form (stage) of the disease. Common signs of the disease are:
- pain syndrome during urination;
- symptoms of intoxication;
- pain in the genital area;
- frequent urge to use the toilet, especially at night;
- possible discharge from the urethra.
As prostatitis progresses in a man, the pain syndrome spreads to other areas. This is due to the transmission of impulses along the nerve endings. The excretion of urine becomes very painful. An acute delay often develops at this stage, which is considered a dangerous condition as it can lead to a rupture of the bladder.
The symptoms of acute prostatitis continue to increase. There is severe pain when defecating, the body temperature rises. The prostate becomes enlarged, tense, and painful. The urine is cloudy due to the pus and mucus it contains.
In the last stage, the disease manifests itself strongly.
The body temperature rises sharply, it is accompanied by fever and chills, loss of appetite, severe weakness and exhaustion of the entire body. Urination may stop completely, and the man will experience acute, severe pain when trying to go to the bathroom. This condition is unbearable, the pain syndrome begins to spread throughout the pelvic area. A man cannot find a place for himself, he is forced to lie with his limbs hidden. When the inflammation has spread to the rectum, mucus will leak from the anus. Yellow-green mucus mixed with blood is released from the urinary tract.
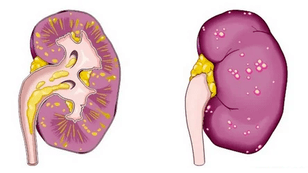
This condition cancause sepsis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, chronic prostatitis, abscess. In this case, urgent hospitalization of the patient and emergency treatment are required.
Diagnosis
Since the symptoms of acute prostatitis in men are very pronounced, the doctor can immediately suspect a pathology. But he needs a thorough examination. A rectal exam is strictly contraindicated in this case.
The urologist must determine the stage (form) of the disease using laboratory and instrumental techniques. The doctor takes aprostate secretfor examination. The concentration of leukocytes in it is increased, which indicates acute inflammation.
Thenlaboratory tests of blood and urine are carried out. The urine is sent to a bacteriological culture for examination, as well as to determine the causative agent of the infection and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. It is also possible:
perform- PCR for STD detection;
- uroflowmetry to identify the severity of organ diseases;
- ultrasound of the prostate to determine the shape and size of the organ, changes in it, the stage of the disease;
- Dopplerometry helps to distinguish acute prostatitis from other pathologies;
- When planning a surgical procedure, an MRI of the pelvic organs is often prescribed.
- Analysis of the SPA concentration in the blood;
- Examination of smears from the urethral discharge;
- Puncture of parts of the organ with suspected purulent infection and abscess.
Treatment
A urologist will explain to you in detail how you can treat acute prostatitis. The main component of therapy is an antibacterial drug, which is selected according to the results of bacterial culture. Within two or three days the antibiotic begins to help, the person feels much better, the pain subsides. However, with this form of the disease, such drugs must be taken for a month, even if the symptoms have completely disappeared.
It is also necessary to prevent the disease from becoming chronic, which is quite common.
When choosing a drug, the doctor takes other factors into account:
- Some active ingredients do not penetrate the tissue of the gland well.
- other active ingredients accumulate in large quantities in the tissue.
Treatment of acute prostatitis in men should be based on the use of strong drugs, as in other cases that threaten a person's life. Doctors usually prescribe fluoroquinolones. When using macrolides, the dosage should be large. This is especially true for patients with immunosuppression.
Antibiotics are usually given with intravenous injections. In the initial stages, the disease can be treated at home or on an outpatient basis.In this case, bed rest is mandatory, as any physical exertion can cause infection to spread and sepsis to develop.
The following drugs are also prescribed in combination with antibiotics:
- analgesics;
- antipyretics;
- NSAIDs;
- An opiate can be prescribed for severe pain.
- diuretics to reduce intoxication of the body;
- laxatives to facilitate bowel movements;
- anti-spasmodic drugs to help you pass urine;
- Alpha blockers.
If a man has acute urinary retention, urea catheterization is performed. Antiandrogens are widely used to reduce swelling and inflammation in the organ, improve the outflow of secretions, normalize blood flow in the gland, and reduce the risk of infection spreading throughout the body.
Using hormones such as estrogen, cold enemas to relieve swelling and pain. Massages and thermal interventions in this form of the disease are strictly prohibited. They can only be used during the recovery period.
surgery
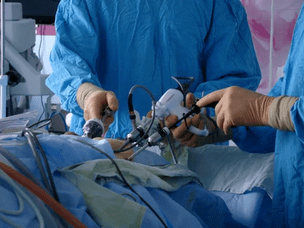
If there is no pain, the doctor may suspect the development of an abscess. In this case, surgical intervention is carried out to eliminate the areas where it appears. Puncture drainage from an abscess is often used. In severe and extreme cases, the organ is removed.
The operation is prescribed in the presence of an abscess, acute urinary retention, severe pain syndrome that cannot be eliminated by drugs, the appearance of stones and neoplasms, as well as ineffectiveness of drug treatment, frequent infections of the genitourinary system and paraproctitis.
The surgeon can use one of the following techniques:
- TRUP (transurethral resection)involves the removal of the inside of the organ. Most used;
- In prostatectomyan organ is partially or completely removed through an incision in the lower abdomen.
- Laser surgery. In this case, the affected areas of the organ are removed with a laser;
- The abscess is drained through the rectum. A drain is inserted into the incision through which the pus is pumped out.
- In order to facilitate urine removal, atransurethral incisionis made in the organ.
When the structure of the glandular tissue is restored, its functions are normalized, the secret of the prostate normalizes its composition, the causative agent of the pathology is completely eliminated from the body, we can talk about the cure of prostatitis.
Forecast
With therapy, the prognosis of the disease will be good. Sometimes negative consequences of acute prostatitis develop. The disease can become chronic, then it is more difficult to get rid of. Organ abscesses, sepsis and acute urinary retention are dangerous consequences of an untreated disease. In some cases, death may occur due to the occurrence of complications. But usually men do not allow such consequences, as they come to the doctor and begin therapy.
Prevention

For prevention, the occurrence of predisposing factors must be prevented. This requires timely treatment of all infections in the body so that they do not become chronic and do not become potential foci of infection that spread to the prostate.
During surgical interventions, the doctor should pay attention to the use of antiseptics. Otherwise, the risk of germs entering the patient's body increases. It is important that a man and his sexual partner treat sexually transmitted diseases in a timely manner, and it is best to prevent their occurrence. Sex life should take place with a regular partner, it should be regular.
It is necessary to lead an active lifestyle, play or play sports, and observe the rules of intimate hygiene.
Men usually seek medical advice in an emergency. However, if negative signs appear, it is better to contact them immediately. This will help prevent many health problems and in some cases even save lives.


























